Question
How do I get the current time in Python?
How do I get the current time in Python?
Question
How do I get the current time in Python?
Solution
Use datetime:
>>> import datetime
>>> now = datetime.datetime.now()
>>> now
datetime.datetime(2009, 1, 6, 15, 8, 24, 78915)
>>> print(now)
2009-01-06 15:08:24.789150
For just the clock time without the date:
>>> now.time()
datetime.time(15, 8, 24, 78915)
>>> print(now.time())
15:08:24.789150
To save typing, you can import the datetime object from the datetime module:
>>> from datetime import datetime
Then remove the prefix datetime. from all of the above.
Solution
Use time.strftime():
>>> from time import gmtime, strftime
>>> strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", gmtime())
'2009-01-05 22:14:39'
Solution
from datetime import datetime
datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
Example output: '2013-09-18 11:16:32'
See list of strftime directives.
Solution
Similar to Harley's answer, but use the str() function for a quick-n-dirty, slightly more human readable format:
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> str(datetime.now())
'2011-05-03 17:45:35.177000'
Solution
How do I get the current time in Python?
time moduleThe time module provides functions that tell us the time in "seconds since the epoch" as well as other utilities.
import time
This is the format you should get timestamps in for saving in databases. It is a simple floating-point number that can be converted to an integer. It is also good for arithmetic in seconds, as it represents the number of seconds since Jan 1, 1970, 00:00:00, and it is memory light relative to the other representations of time we'll be looking at next:
>>> time.time()
1424233311.771502
This timestamp does not account for leap-seconds, so it's not linear - leap seconds are ignored. So while it is not equivalent to the international UTC standard, it is close, and therefore quite good for most cases of record-keeping.
This is not ideal for human scheduling, however. If you have a future event you wish to take place at a certain point in time, you'll want to store that time with a string that can be parsed into a datetime object or a serialized datetime object (these will be described later).
time.ctimeYou can also represent the current time in the way preferred by your operating system (which means it can change when you change your system preferences, so don't rely on this to be standard across all systems, as I've seen others expect). This is typically user friendly, but doesn't typically result in strings one can sort chronologically:
>>> time.ctime()
'Tue Feb 17 23:21:56 2015'
You can hydrate timestamps into human readable form with ctime as well:
>>> time.ctime(1424233311.771502)
'Tue Feb 17 23:21:51 2015'
This conversion is also not good for record-keeping (except in text that will only be parsed by humans - and with improved Optical Character Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, I think the number of these cases will diminish).
datetime moduleThe datetime module is also quite useful here:
>>> import datetime
datetime.datetime.nowThe datetime.now is a class method that returns the current time. It uses the time.localtime without the timezone info (if not given, otherwise see timezone aware below). It has a representation (which would allow you to recreate an equivalent object) echoed on the shell, but when printed (or coerced to a str), it is in human readable (and nearly ISO) format, and the lexicographic sort is equivalent to the chronological sort:
>>> datetime.datetime.now()
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 17, 23, 43, 49, 94252)
>>> print(datetime.datetime.now())
2015-02-17 23:43:51.782461
utcnowYou can get a datetime object in UTC time, a global standard, by doing this:
>>> datetime.datetime.utcnow()
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 18, 4, 53, 28, 394163)
>>> print(datetime.datetime.utcnow())
2015-02-18 04:53:31.783988
UTC is a time standard that is nearly equivalent to the GMT timezone. (While GMT and UTC do not change for Daylight Savings Time, their users may switch to other timezones, like British Summer Time, during the Summer.)
However, none of the datetime objects we've created so far can be easily converted to various timezones. We can solve that problem with the pytz module:
>>> import pytz
>>> then = datetime.datetime.now(pytz.utc)
>>> then
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 18, 4, 55, 58, 753949, tzinfo=<UTC>)
Equivalently, in Python 3 we have the timezone class with a utc timezone instance attached, which also makes the object timezone aware (but to convert to another timezone without the handy pytz module is left as an exercise to the reader):
>>> datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone.utc)
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 18, 22, 31, 56, 564191, tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc)
And we see we can easily convert to timezones from the original UTC object.
>>> print(then)
2015-02-18 04:55:58.753949+00:00
>>> print(then.astimezone(pytz.timezone('US/Eastern')))
2015-02-17 23:55:58.753949-05:00
You can also make a naive datetime object aware with the pytz timezone localize method, or by replacing the tzinfo attribute (with replace, this is done blindly), but these are more last resorts than best practices:
>>> pytz.utc.localize(datetime.datetime.utcnow())
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 18, 6, 6, 29, 32285, tzinfo=<UTC>)
>>> datetime.datetime.utcnow().replace(tzinfo=pytz.utc)
datetime.datetime(2015, 2, 18, 6, 9, 30, 728550, tzinfo=<UTC>)
The pytz module allows us to make our datetime objects timezone aware and convert the times to the hundreds of timezones available in the pytz module.
One could ostensibly serialize this object for UTC time and store that in a database, but it would require far more memory and be more prone to error than simply storing the Unix Epoch time, which I demonstrated first.
The other ways of viewing times are much more error-prone, especially when dealing with data that may come from different time zones. You want there to be no confusion as to which timezone a string or serialized datetime object was intended for.
If you're displaying the time with Python for the user, ctime works nicely, not in a table (it doesn't typically sort well), but perhaps in a clock. However, I personally recommend, when dealing with time in Python, either using Unix time, or a timezone aware UTC datetime object.
Solution
Do
from time import time
t = time()
t - float number, good for time interval measurement.There is some difference for Unix and Windows platforms.
Solution
>>> from time import gmtime, strftime
>>> strftime("%a, %d %b %Y %X +0000", gmtime())
'Tue, 06 Jan 2009 04:54:56 +0000'
That outputs the current GMT in the specified format. There is also a localtime() method.
This page has more details.
Solution
The previous answers are all good suggestions, but I find it easiest to use ctime():
In [2]: from time import ctime
In [3]: ctime()
Out[3]: 'Thu Oct 31 11:40:53 2013'
This gives a nicely formatted string representation of the current local time.
Solution
The quickest way is:
>>> import time
>>> time.strftime("%Y%m%d")
'20130924'
Solution
If you need current time as a time object:
>>> import datetime
>>> now = datetime.datetime.now()
>>> datetime.time(now.hour, now.minute, now.second)
datetime.time(11, 23, 44)
Solution
You can use the time module:
>>> import time
>>> print(time.strftime("%d/%m/%Y"))
06/02/2015
The use of the capital Y gives the full year, and using y would give 06/02/15.
You could also use the following code to give a more lengthy time:
>>> time.strftime("%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S")
'Fri, 06 Feb 2015 17:45:09'
Solution
.isoformat() is in the documentation, but not yet here
(this is mighty similar to @Ray Vega's answer):
>>> import datetime
>>> datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
'2013-06-24T20:35:55.982000'
Solution
Why not ask the U.S. Naval Observatory, the official timekeeper of the United States Navy?
import requests
from lxml import html
page = requests.get('http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/cgi-bin/timer.pl')
tree = html.fromstring(page.content)
print(tree.xpath('//html//body//h3//pre/text()')[1])
If you live in the D.C. area (like me) the latency might not be too bad...
Solution
Using pandas to get the current time, kind of overkilling the problem at hand:
import pandas as pd
print(pd.datetime.now())
print(pd.datetime.now().date())
print(pd.datetime.now().year)
print(pd.datetime.now().month)
print(pd.datetime.now().day)
print(pd.datetime.now().hour)
print(pd.datetime.now().minute)
print(pd.datetime.now().second)
print(pd.datetime.now().microsecond)
Output:
2017-09-22 12:44:56.092642
2017-09-22
2017
9
22
12
44
56
92693
Solution
if you are using numpy already then directly you can use numpy.datetime64() function.
import numpy as np
str(np.datetime64('now'))
for only date:
str(np.datetime64('today'))
or, if you are using pandas already then you can use pandas.to_datetime() function
import pandas as pd
str(pd.to_datetime('now'))
or,
str(pd.to_datetime('today'))
Solution
This is what I ended up going with:
>>>from time import strftime
>>>strftime("%m/%d/%Y %H:%M")
01/09/2015 13:11
Also, this table is a necessary reference for choosing the appropriate format codes to get the date formatted just the way you want it (from Python "datetime" documentation here).
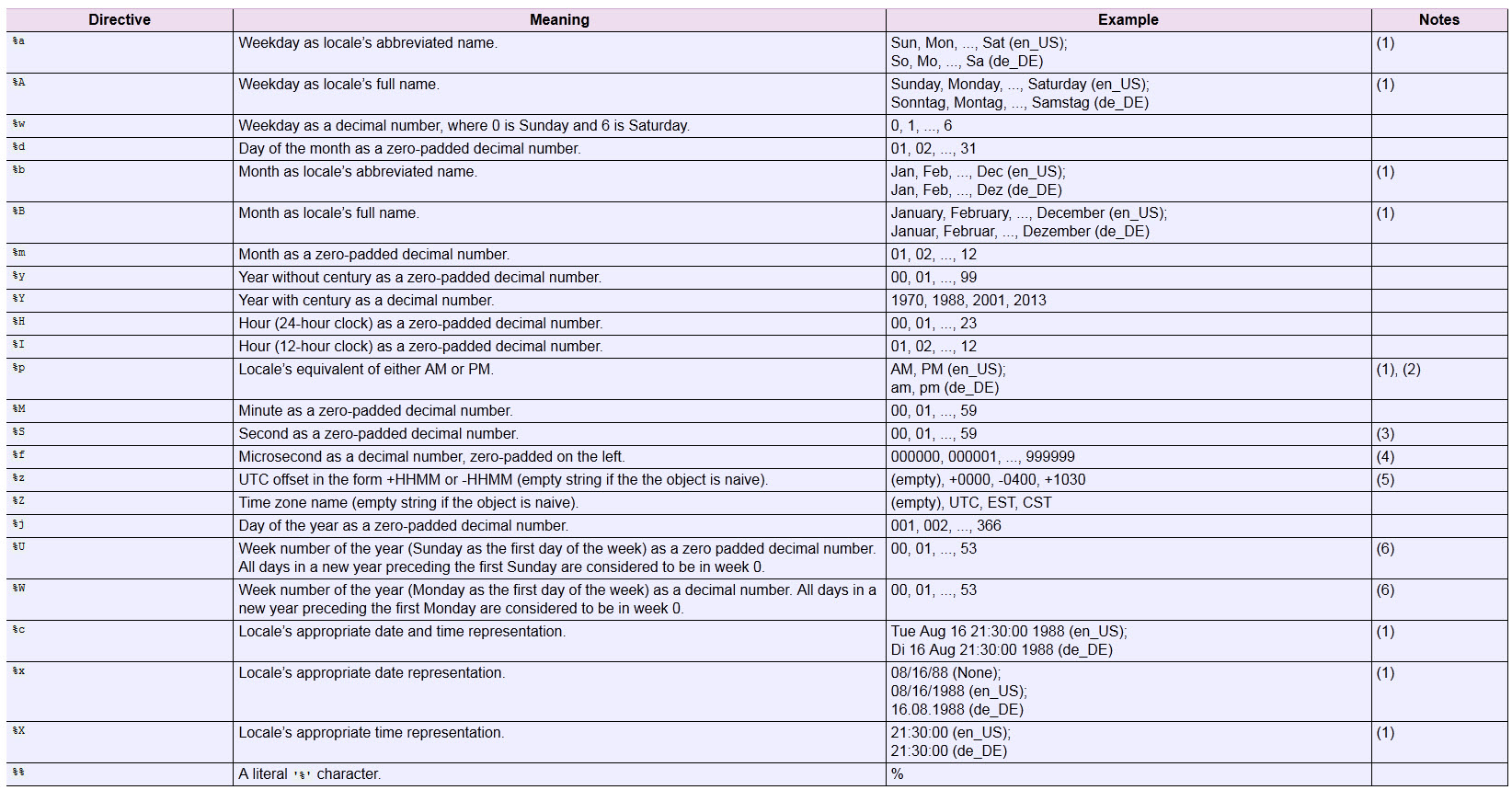
Solution
datetime.now() returns the current time as a naive datetime object that represents time in the local timezone. That value may be ambiguous e.g., during DST transitions ("fall back"). To avoid ambiguity either UTC timezone should be used:
from datetime import datetime
utc_time = datetime.utcnow()
print(utc_time) # -> 2014-12-22 22:48:59.916417
Or a timezone-aware object that has the corresponding timezone info attached (Python 3.2+):
from datetime import datetime, timezone
now = datetime.now(timezone.utc).astimezone()
print(now) # -> 2014-12-23 01:49:25.837541+03:00
Solution
This question doesn't need a new answer just for the sake of it ... a shiny new-ish toy/module, however, is enough justification. That being the Pendulum library, which appears to do the sort of things which arrow attempted, except without the inherent flaws and bugs which beset arrow.
For instance, the answer to the original question:
>>> import pendulum
>>> print(pendulum.now())
2018-08-14T05:29:28.315802+10:00
>>> print(pendulum.now('utc'))
2018-08-13T19:29:35.051023+00:00
There's a lot of standards which need addressing, including multiple RFCs and ISOs, to worry about. Ever get them mixed up; not to worry, take a little look into dir(pendulum.constants) There's a bit more than RFC and ISO formats there, though.
When we say local, though what do we mean? Well I mean:
>>> print(pendulum.now().timezone_name)
Australia/Melbourne
>>>
Presumably most of the rest of you mean somewhere else.
And on it goes. Long story short: Pendulum attempts to do for date and time what requests did for HTTP. It's worth consideration, particularly for both its ease of use and extensive documentation.
Solution
>>> import datetime, time
>>> time = time.strftime("%H:%M:%S:%MS", time.localtime())
>>> print time
'00:21:38:20S'
Solution
import datetime
date_time = datetime.datetime.now()
date = date_time.date() # Gives the date
time = date_time.time() # Gives the time
print date.year, date.month, date.day
print time.hour, time.minute, time.second, time.microsecond
Do dir(date) or any variables including the package. You can get all the attributes and methods associated with the variable.
Solution
By default, now() function returns output in the YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS:MS format. Use the below sample script to get the current date and time in a Python script and print results on the screen. Create file getDateTime1.py with the below content.
import datetime
currentDT = datetime.datetime.now()
print (str(currentDT))
The output looks like below:
2018-03-01 17:03:46.759624
Solution
Try the arrow module from http://crsmithdev.com/arrow/:
import arrow
arrow.now()
Or the UTC version:
arrow.utcnow()
To change its output, add .format():
arrow.utcnow().format('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss ZZ')
For a specific timezone:
arrow.now('US/Pacific')
An hour ago:
arrow.utcnow().replace(hours=-1)
Or if you want the gist.
arrow.get('2013-05-11T21:23:58.970460+00:00').humanize()
>>> '2 years ago'
Solution
To get exactly 3 decimal points for milliseconds 11:34:23.751 run this:
def get_time_str(decimal_points=3):
return time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) + '.%d' % (time.time() % 1 * 10**decimal_points)
More context:
I want to get the time with milliseconds. A simple way to get them:
import time, datetime
print(datetime.datetime.now().time()) # 11:20:08.272239
# Or in a more complicated way
print(datetime.datetime.now().time().isoformat()) # 11:20:08.272239
print(datetime.datetime.now().time().strftime('%H:%M:%S.%f')) # 11:20:08.272239
# But do not use this:
print(time.strftime("%H:%M:%S.%f", time.localtime()), str) # 11:20:08.%f
But I want only milliseconds, right? The shortest way to get them:
import time
time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) + '.%d' % (time.time() % 1 * 1000)
# 11:34:23.751
Add or remove zeroes from the last multiplication to adjust number of decimal points, or just:
def get_time_str(decimal_points=3):
return time.strftime("%H:%M:%S", time.localtime()) + '.%d' % (time.time() % 1 * 10**decimal_points)
Solution
Current time of a timezone
from datetime import datetime
import pytz
tz_NY = pytz.timezone('America/New_York')
datetime_NY = datetime.now(tz_NY)
print("NY time:", datetime_NY.strftime("%H:%M:%S"))
tz_London = pytz.timezone('Europe/London')
datetime_London = datetime.now(tz_London)
print("London time:", datetime_London.strftime("%H:%M:%S"))
tz_India = pytz.timezone('Asia/India')
datetime_India = datetime.now(tz_India)
print("India time:", datetime_India.strftime("%H:%M:%S"))
#list timezones
pytz.all_timezones
Solution
You can use this function to get the time (unfortunately it doesn't say AM or PM):
def gettime():
from datetime import datetime
return ((str(datetime.now())).split(' ')[1]).split('.')[0]
To get the hours, minutes, seconds and milliseconds to merge later, you can use these functions:
Hour:
def gethour():
from datetime import datetime
return (((str(datetime.now())).split(' ')[1]).split('.')[0]).split(':')[0]
Minute:
def getminute():
from datetime import datetime
return (((str(datetime.now())).split(' ')[1]).split('.')[0]).split(':')[1]
Second:
def getsecond():
from datetime import datetime
return (((str(datetime.now())).split(' ')[1]).split('.')[0]).split(':')[2]
Millisecond:
def getmillisecond():
from datetime import datetime
return (str(datetime.now())).split('.')[1]
Solution
If you just want the current timestamp in ms (for example, to measure execution time), you can also use the "timeit" module:
import timeit
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
do_stuff_you_want_to_measure()
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print("Elapsed time: {}".format(end_time - start_time))
Solution
You can try the following
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print(now)
or
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print(now.strftime("%Y-%b-%d, %A %I:%M:%S"))
Solution
Because no one has mentioned it yet, and this is something I ran into recently... a pytz timezone's fromutc() method combined with datetime's utcnow() is the best way I've found to get a useful current time (and date) in any timezone.
from datetime import datetime
import pytz
JST = pytz.timezone("Asia/Tokyo")
local_time = JST.fromutc(datetime.utcnow())
If all you want is the time, you can then get that with local_time.time().
Solution
import datetime
todays_date = datetime.date.today()
print(todays_date)
>>> 2019-10-12
# adding strftime will remove the seconds
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M')
print(current_time)
>>> 23:38
Solution
Method1: Getting Current Date and Time from system datetime
The datetime module supplies classes for manipulating dates and times.
Code
from datetime import datetime,date
print("Date: "+str(date.today().year)+"-"+str(date.today().month)+"-"+str(date.today().day))
print("Year: "+str(date.today().year))
print("Month: "+str(date.today().month))
print("Day: "+str(date.today().day)+"\n")
print("Time: "+str(datetime.today().hour)+":"+str(datetime.today().minute)+":"+str(datetime.today().second))
print("Hour: "+str(datetime.today().hour))
print("Minute: "+str(datetime.today().minute))
print("Second: "+str(datetime.today().second))
print("MilliSecond: "+str(datetime.today().microsecond))
Output will be like
Date: 2020-4-18
Year: 2020
Month: 4
Day: 18
Time: 19:30:5
Hour: 19
Minute: 30
Second: 5
MilliSecond: 836071
Method2: Getting Current Date and Time if Network is available
urllib package helps us to handle the url's that means webpages. Here we collects data from the webpage http://just-the-time.appspot.com/ and parses dateime from the webpage using the package dateparser.
Code
from urllib.request import urlopen
import dateparser
time_url = urlopen(u'http://just-the-time.appspot.com/')
datetime = time_url.read().decode("utf-8", errors="ignore").split(' ')[:-1]
date = datetime[0]
time = datetime[1]
print("Date: "+str(date))
print("Year: "+str(date.split('-')[0]))
print("Month: "+str(date.split('-')[1]))
print("Day: "+str(date.split('-')[2])+'\n')
print("Time: "+str(time))
print("Hour: "+str(time.split(':')[0]))
print("Minute: "+str(time.split(':')[1]))
print("Second: "+str(time.split(':')[2]))
Output will be like
Date: 2020-04-18
Year: 2020
Month: 04
Day: 18
Time: 14:17:10
Hour: 14
Minute: 17
Second: 10
Method3: Getting Current Date and Time from Local Time of the Machine
Python's time module provides a function for getting local time from the number of seconds elapsed since the epoch called localtime(). ctime() function takes seconds passed since epoch as an argument and returns a string representing local time.
Code
from time import time, ctime
datetime = ctime(time()).split(' ')
print("Date: "+str(datetime[4])+"-"+str(datetime[1])+"-"+str(datetime[2]))
print("Year: "+str(datetime[4]))
print("Month: "+str(datetime[1]))
print("Day: "+str(datetime[2]))
print("Week Day: "+str(datetime[0])+'\n')
print("Time: "+str(datetime[3]))
print("Hour: "+str(datetime[3]).split(':')[0])
print("Minute: "+str(datetime[3]).split(':')[1])
print("Second: "+str(datetime[3]).split(':')[2])
Output will be like
Date: 2020-Apr-18
Year: 2020
Month: Apr
Day: 18
Week Day: Sat
Time: 19:30:20
Hour: 19
Minute: 30
Second: 20